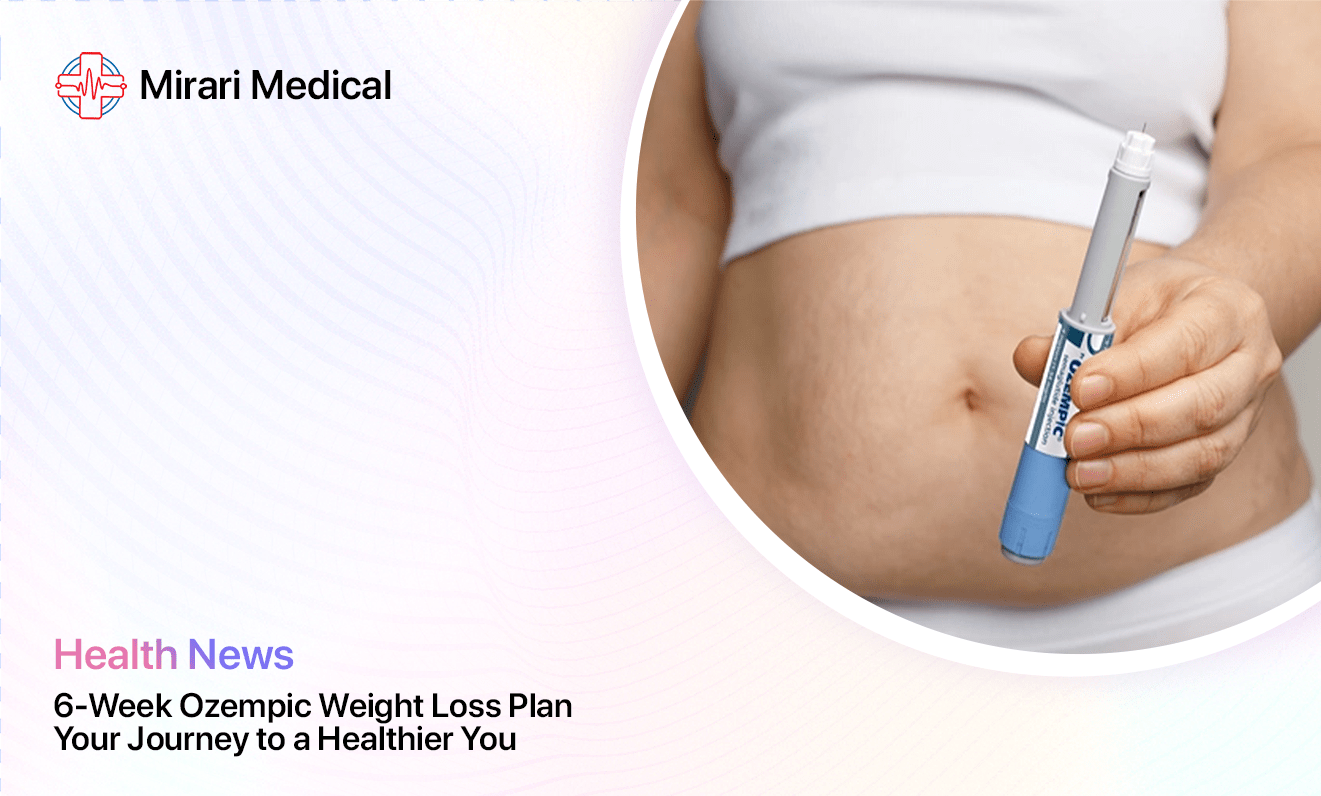
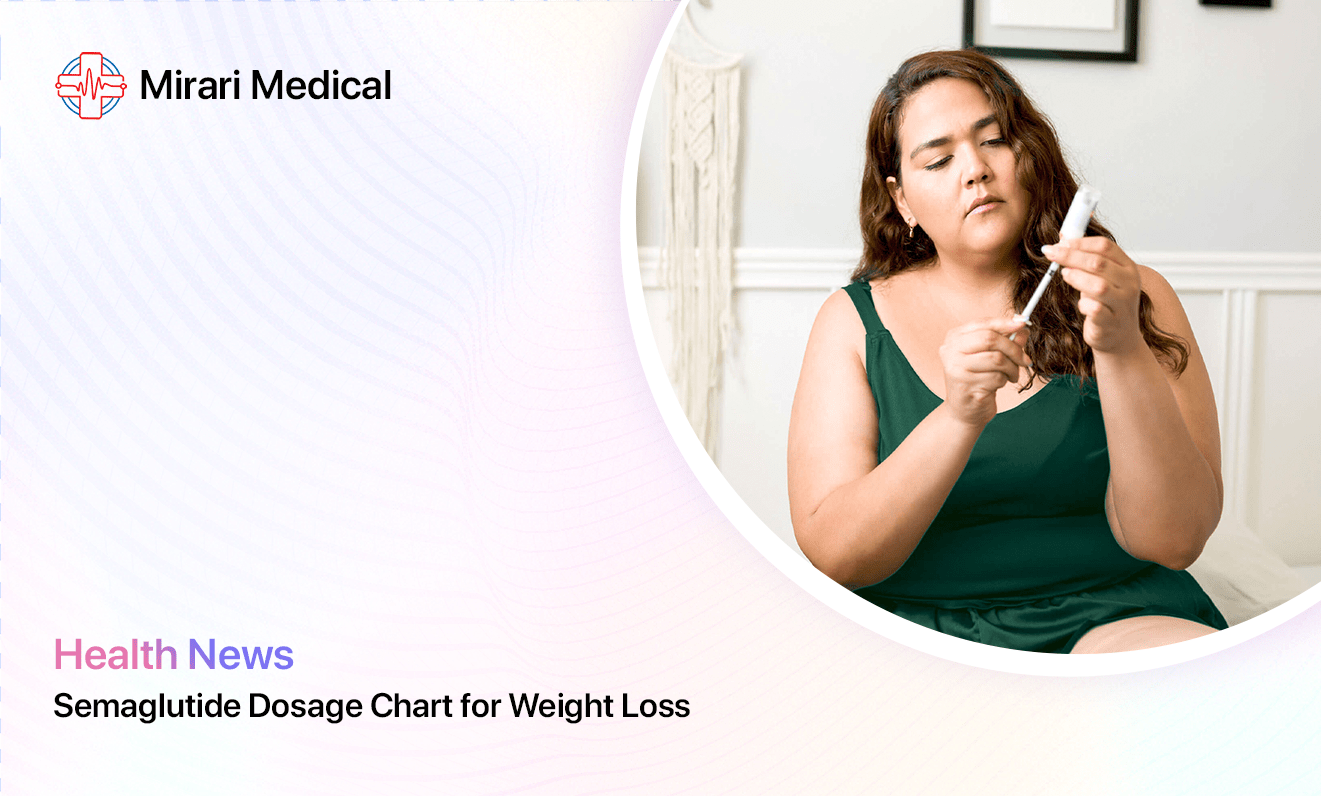
Semaglutide Dosage Chart for Weight Loss
You may be interested
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist that was initially developed to treat type 2 diabetes. However, researchers discovered its remarkable potential for weight loss, leading to its approval by the FDA for chronic weight management in adults with obesity or overweight with at least one weight-related comorbidity[1].
As with any medication, proper dosing is crucial for achieving optimal results while minimizing side effects. The semaglutide dosage chart for weight loss provides a structured approach to initiating and maintaining treatment. Let’s dive into the details of this dosing schedule and explore how it can help you on your weight loss journey.
Initial Dose Escalation Schedule
The key to successful semaglutide treatment lies in a gradual dose escalation. This approach allows your body to adjust to the medication, reducing the likelihood of side effects. The initial dose escalation schedule typically spans 16 weeks, divided into four-week intervals.
Weeks 1-4
During the first month of treatment, you’ll start with the lowest dose of semaglutide. This introductory period is crucial for assessing your body’s response to the medication.
- Dosage: 0.25 mg once weekly
- Administration: Subcutaneous injection
- Purpose: To allow your body to acclimate to the medication and minimize initial side effects
It’s important to note that this initial dose is not expected to provide significant weight loss. Instead, it serves as a starting point to build tolerance to the medication. You may experience mild side effects during this period, such as nausea or digestive discomfort. These symptoms are typically temporary and should improve as your body adjusts.
Pro tip: Keep a journal during these first few weeks to track any side effects or changes you notice. This information can be valuable when discussing your progress with your healthcare provider.
Weeks 5-8
As you enter the second month of treatment, your healthcare provider will likely increase your dosage. This step-up in medication aims to enhance the weight loss effects while still maintaining a manageable level of side effects.
- Dosage: 0.5 mg once weekly
- Administration: Subcutaneous injection
- Purpose: To begin experiencing more noticeable effects on appetite and weight
During this phase, you may start to notice changes in your appetite and eating habits. Many people report feeling fuller faster and experiencing reduced cravings. It’s essential to capitalize on these effects by maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise routine.
Remember: Semaglutide is not a magic solution but rather a tool to support your weight loss efforts. Combining the medication with lifestyle changes will yield the best results.
Weeks 9-12
The third month of treatment brings another increase in dosage, further amplifying the weight loss effects of semaglutide.
- Dosage: 1.0 mg once weekly
- Administration: Subcutaneous injection
- Purpose: To enhance weight loss effects and continue progress towards the target dose
At this stage, many people begin to see more significant weight loss. You may notice changes in your body composition and improvements in weight-related health markers, such as blood pressure or blood sugar levels.
Important note: If you experience persistent or severe side effects at this dosage, don’t hesitate to discuss them with your healthcare provider. They may recommend adjusting the dose or exploring other options to manage side effects.
Weeks 13-16
The final stage of the initial dose escalation brings you to the penultimate dose before reaching the maintenance level.
- Dosage: 1.7 mg once weekly
- Administration: Subcutaneous injection
- Purpose: To prepare your body for the full maintenance dose and maximize weight loss effects
During these weeks, you should be experiencing the full benefits of semaglutide treatment. Your appetite should be significantly reduced, and you may find it easier to adhere to a calorie-controlled diet. Continue to focus on healthy eating habits and regular physical activity to optimize your results.
Tip: Use this time to solidify healthy habits that will support your long-term weight management goals. The skills you develop now will be crucial for maintaining your weight loss after reaching your target.
Maintenance Dose
After completing the 16-week dose escalation period, you’ll transition to the maintenance phase of semaglutide treatment. This stage is designed to help you continue losing weight or maintain your weight loss over the long term.
Week 17 and Onward
The maintenance dose represents the maximum recommended dosage for weight loss treatment with semaglutide.
- Dosage: 2.4 mg once weekly
- Administration: Subcutaneous injection
- Purpose: To provide ongoing support for weight loss and weight maintenance
At this dosage, semaglutide exerts its full effect on appetite regulation and metabolism. Many people continue to lose weight during the maintenance phase, albeit at a slower rate than during the initial treatment period.
It’s important to understand that the duration of maintenance treatment can vary depending on individual factors and treatment goals. Some people may continue semaglutide treatment indefinitely, while others may eventually transition off the medication under their healthcare provider’s guidance.
Key point: Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are essential during the maintenance phase to monitor your progress, assess any side effects, and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
Dosing Considerations
While the semaglutide dosage chart for weight loss provides a general framework for treatment, it’s important to recognize that individual responses to the medication can vary. Your healthcare provider may need to make adjustments based on your specific needs and circumstances.
Dose Escalation Tolerance
Not everyone will tolerate the standard dose escalation schedule. If you experience significant side effects or have difficulty adjusting to a higher dose, your healthcare provider may recommend a more gradual approach.
- Extended escalation: Some patients may benefit from spending additional time at lower doses before moving up to the next level.
- Smaller increments: In some cases, your provider might use smaller dose increases, such as 0.25 mg increments, to find the optimal balance between efficacy and tolerability.
Remember: Open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial. Don’t hesitate to report any concerns or side effects you experience during the dose escalation process.
Maintenance Dose Tolerance
While 2.4 mg is the target maintenance dose for most patients, some individuals may achieve satisfactory results at lower doses or require adjustments due to side effects.
- Lower maintenance dose: If you’re experiencing good weight loss results and minimal side effects at a lower dose (e.g., 1.7 mg), your provider may recommend staying at that level rather than increasing to 2.4 mg.
- Dose reduction: If side effects become problematic at the 2.4 mg dose, your provider may temporarily reduce the dose to 1.7 mg to improve tolerability.
Important: Any changes to your dosing schedule should be made under the guidance of your healthcare provider. Never adjust your dose on your own.
Missed Dose Guidelines
Consistency is key when it comes to semaglutide treatment. However, if you miss a dose, follow these guidelines:
- If less than 5 days have passed since the missed dose, take it as soon as you remember.
- If more than 5 days have passed, skip the missed dose and take your next scheduled dose.
- Never take a double dose to make up for a missed one.
Pro tip: Set a weekly reminder on your phone or use a medication tracking app to help you stay on schedule with your semaglutide injections.
Contraindications
While semaglutide can be an effective weight loss tool for many people, there are certain conditions and circumstances where its use is not recommended. Understanding these contraindications is crucial for ensuring your safety and the appropriateness of semaglutide treatment.
History of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC)
Semaglutide is contraindicated in individuals with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). This rare type of thyroid cancer requires special consideration when it comes to GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide.
- Reason for contraindication: Animal studies have shown an increased risk of thyroid C-cell tumors with GLP-1 receptor agonists. While it’s unclear if this risk applies to humans, the precautionary principle is applied.
- What to do: If you have a history of MTC or know of family members who have had this condition, inform your healthcare provider immediately. They will likely recommend alternative weight loss strategies.
Important note: Regular thyroid monitoring may be recommended for patients on semaglutide, especially those with risk factors for thyroid disorders.
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome Type 2 (MEN 2)
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome Type 2 (MEN 2) is a rare genetic condition that increases the risk of several types of endocrine tumors, including MTC.
- Reason for contraindication: Due to the increased risk of MTC in individuals with MEN 2, semaglutide is not recommended for this population.
- What to do: If you have been diagnosed with MEN 2 or have a family history of this condition, discuss this with your healthcare provider before considering semaglutide treatment.
Key point: Genetic testing may be recommended for individuals with a family history of MEN 2 before initiating semaglutide treatment.
Hypersensitivity to Semaglutide
As with any medication, some individuals may have an allergic reaction or hypersensitivity to semaglutide or its components.
- Reason for contraindication: Allergic reactions can range from mild skin irritation to severe, life-threatening anaphylaxis.
- What to do: If you’ve had an allergic reaction to semaglutide or other GLP-1 receptor agonists in the past, inform your healthcare provider. They will likely recommend alternative weight loss medications or strategies.
Signs of an allergic reaction: Watch for symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling (especially of the face, tongue, or throat), severe dizziness, or difficulty breathing. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Precautions
While semaglutide can be an effective tool for weight loss, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and take necessary precautions. Your healthcare provider will consider these factors when determining if semaglutide is appropriate for you and how to monitor your treatment.
Risk of Thyroid C-Cell Tumors
One of the most significant precautions associated with semaglutide use is the potential risk of thyroid C-cell tumors. This concern stems from animal studies, although it’s important to note that the relevance to humans is not fully understood.
- Monitoring: Your healthcare provider may recommend periodic thyroid function tests and physical examinations to check for any signs of thyroid abnormalities.
- Symptoms to watch for: Be alert for symptoms such as a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, shortness of breath, or persistent hoarseness. Report any of these symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
Important: While the risk of thyroid tumors in humans is not confirmed, this precaution underscores the importance of using semaglutide only under close medical supervision.
Potential for Gastrointestinal (GI) Adverse Reactions
Gastrointestinal side effects are among the most common issues reported by people taking semaglutide. These effects are typically mild to moderate and often improve over time, but they can be bothersome for some individuals.
- Common GI side effects: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and constipation
- Management strategies:
- Start with a low dose and gradually increase as tolerated
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
- Stay well-hydrated
- Avoid fatty or spicy foods that may exacerbate symptoms
Pro tip: Keep a food diary to identify any triggers that worsen your GI symptoms. This information can be valuable in developing strategies to minimize discomfort.
Risk of Pancreatitis
While rare, there is a potential risk of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) associated with semaglutide use. This risk is particularly important to consider for individuals with a history of pancreatic issues.
- Symptoms to watch for: Severe abdominal pain that may radiate to the back, nausea, vomiting, and fever
- What to do: If you experience these symptoms, stop taking semaglutide and seek medical attention immediately
Important note: Your healthcare provider may recommend periodic monitoring of pancreatic enzymes, especially if you have risk factors for pancreatitis.
Monitoring for Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
There have been reports of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in some patients taking GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide. While a direct causal relationship has not been established, it’s important to be aware of this potential risk.
- Who may be at risk: Individuals with a history of depression or other mental health disorders may be more susceptible
- What to watch for: Changes in mood, thoughts of self-harm, or unusual behavioral changes
- What to do: If you experience these symptoms or notice them in a loved one taking semaglutide, contact a healthcare provider immediately
Remember: Mental health is an important aspect of overall well-being. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
Administration Instructions
Proper administration of semaglutide is crucial for ensuring its effectiveness and minimizing potential side effects. Following these instructions carefully will help you get the most out of your treatment while maintaining safety.
Subcutaneous Injection Technique
Semaglutide is administered via subcutaneous injection, which means it’s injected into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin. Here’s a step-by-step guide to proper injection technique:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Choose an injection site: Suitable areas include the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm.
- Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab and let it dry completely.
- Prepare the pen: Remove the pen cap and attach a new needle.
- Prime the pen: For first-time use of a new pen, perform a flow check by dialing to the flow check symbol and pressing the dose button until a drop appears at the needle tip.
- Set the dose: Turn the dose selector to your prescribed dose.
- Insert the needle: Pinch the skin at the injection site and insert the needle at a 90-degree angle.
- Inject the medication: Press and hold the dose button until the dose counter shows 0.
- Count to 6: Keep the needle in place and continue holding the dose button for 6 seconds to ensure the full dose is delivered.
- Remove and dispose: Carefully remove the needle and dispose of it in a sharps container.
Pro tip: If you’re nervous about self-injecting, ask your healthcare provider or a diabetes educator for a demonstration and practice session.
Injection Site Rotation
To prevent lipodystrophy (changes in fat tissue at the injection site) and maintain consistent absorption of the medication, it’s important to rotate your injection sites.
- Create a rotation plan: Divide your injection areas into sections and move systematically through them.
- Keep track: Use an injection site rotation chart or app to log where you’ve injected.
- Spacing: Keep at least 1 inch between injection sites.
Remember: Never inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, scarred, or hardened.
Administration with Insulin
If you’re also using insulin, there are some important considerations to keep in mind:
- Separate injections: Always use separate injection sites for semaglutide and insulin.
- Timing: You can inject semaglutide and insulin at the same time of day, but don’t mix them in the same syringe.
- Blood sugar monitoring: Be aware that semaglutide can affect your blood sugar levels. Your insulin dosage may need adjustment under your healthcare provider’s guidance.
Important: Always consult with your healthcare provider about the proper management of multiple injectable medications.
Storage Requirements
Proper storage of semaglutide is essential for maintaining its effectiveness:
- Unopened pens: Store in the refrigerator (36°F to 46°F or 2°C to 8°C).
- In-use pens: Can be stored at room temperature (below 86°F or 30°C) or in the refrigerator for up to 56 days.
- Do not freeze: Discard the pen if it has been frozen.
-
- Protect from light: Keep the pen cap on when not in use to protect the medication from light.
- Travel considerations: When traveling, use a cooler bag with ice packs to maintain the proper temperature.
Pro tip: Set a reminder to check the expiration date of your semaglutide pens regularly. Discard any medication that has expired or been improperly stored.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial components of successful semaglutide treatment for weight loss. These check-ins allow your healthcare provider to assess your progress, manage any side effects, and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Blood Glucose Monitoring
While semaglutide is primarily used for weight loss in non-diabetic individuals, it can affect blood sugar levels. Regular monitoring is important, especially if you have a history of diabetes or prediabetes.
- Frequency: Your healthcare provider will recommend a monitoring schedule based on your individual needs.
- What to watch for: Look for patterns of high or low blood sugar readings.
- Reporting: Keep a log of your blood glucose readings to share with your healthcare provider during follow-up appointments.
Important note: If you experience symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) such as dizziness, sweating, or confusion, check your blood sugar immediately and follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for managing low blood sugar.
Renal Function Monitoring
Semaglutide can potentially affect kidney function, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney issues. Regular monitoring of renal function is important to ensure the medication isn’t causing any adverse effects.
- Tests: Your healthcare provider may order periodic blood tests to check creatinine levels and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
- Frequency: The frequency of these tests will depend on your individual risk factors and medical history.
- What to do: If you notice any changes in urination patterns or experience swelling in your legs or feet, report these symptoms to your healthcare provider promptly.
Remember: Staying well-hydrated is important for maintaining good kidney function, especially when taking medications like semaglutide.
Heart Rate Monitoring
Semaglutide can cause an increase in heart rate in some individuals. While this is generally not a cause for concern, it’s important to monitor your heart rate regularly.
- How to monitor: You can check your pulse manually or use a heart rate monitor or fitness tracker.
- When to check: Measure your resting heart rate in the morning before getting out of bed.
- What’s normal: A normal resting heart rate for adults is typically between 60-100 beats per minute.
Pro tip: If you notice a consistent increase in your resting heart rate or experience palpitations, inform your healthcare provider.
Thyroid Tumor Monitoring
Due to the potential risk of thyroid C-cell tumors associated with semaglutide, ongoing monitoring of thyroid function is important.
- Physical exams: Your healthcare provider may perform regular neck examinations to check for any lumps or swelling.
- Blood tests: Periodic blood tests may be ordered to check thyroid hormone levels.
- Symptoms to watch for: Report any persistent hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, or neck discomfort to your healthcare provider immediately.
Key point: While the risk of thyroid tumors in humans is not confirmed, this monitoring is a precautionary measure to ensure your safety during treatment.
Diabetic Retinopathy Monitoring
For individuals with a history of diabetes, regular eye exams are crucial when starting semaglutide treatment. Rapid improvements in blood sugar control can sometimes worsen diabetic retinopathy in the short term.
- Baseline exam: If you have diabetes, your healthcare provider may recommend a comprehensive eye exam before starting semaglutide.
- Follow-up exams: Regular eye check-ups should be scheduled as recommended by your eye care professional.
- Symptoms to watch for: Report any changes in vision, such as blurriness or dark spots, to your healthcare provider promptly.
Remember: Even if you don’t have diabetes, regular eye exams are an important part of overall health maintenance.
Patient Advice
Successful treatment with semaglutide involves more than just taking the medication as prescribed. Here are some important pieces of advice to help you navigate your weight loss journey safely and effectively.
Importance of Patient Labeling
Always read and follow the patient information leaflet that comes with your semaglutide prescription. This document contains crucial information about:
- Proper dosing and administration
- Potential side effects and how to manage them
- Storage requirements
- When to seek medical attention
Pro tip: Keep the patient information leaflet in a safe, easily accessible place for quick reference. Consider taking a photo of it with your smartphone for easy access on the go.
Needle Sharing and Transmission of Blood-Borne Pathogens
Semaglutide is administered via a pen injector with disposable needles. It’s crucial to follow proper safety protocols to prevent the transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
- Never share needles: Each needle should be used only once and by only one person.
- Proper disposal: Always dispose of used needles in a designated sharps container.
- Needle safety: Replace the pen cap after each use to prevent accidental needle sticks.
Important: If you accidentally use a needle that someone else has used, contact your healthcare provider immediately for guidance on necessary precautions or testing.
Reporting Symptoms of Thyroid Tumors
While the risk of thyroid tumors in humans taking semaglutide is not confirmed, it’s important to be vigilant about potential symptoms. Report any of the following to your healthcare provider promptly:
- A lump or swelling in the neck
- Hoarseness that doesn’t go away
- Trouble swallowing
- Shortness of breath
Remember: These symptoms don’t necessarily mean you have a thyroid tumor, but they warrant prompt medical evaluation.
Managing Gastrointestinal Side Effects
Gastrointestinal side effects are common when starting semaglutide treatment. Here are some strategies to help manage these symptoms:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals: This can help reduce nausea and feelings of fullness.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially if you’re experiencing diarrhea.
- Avoid trigger foods: Keep a food diary to identify any foods that worsen your symptoms.
- Consider timing: Some people find that taking semaglutide at bedtime helps minimize daytime nausea.
Pro tip: Talk to your healthcare provider about over-the-counter remedies that may help alleviate mild GI symptoms.
Recognizing and Managing Hypoglycemia
While semaglutide is not typically associated with hypoglycemia in non-diabetic individuals, it’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms, especially if you’re also taking other medications that can affect blood sugar levels.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia include:
- Shakiness
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Confusion
- Irritability
- Hunger
If you experience these symptoms:
- Check your blood sugar if possible
- Consume 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates (e.g., glucose tablets, fruit juice)
- Recheck your blood sugar after 15 minutes
- Repeat treatment if blood sugar remains low
Important: If you experience frequent episodes of hypoglycemia, inform your healthcare provider as your treatment plan may need adjustment.
Pregnancy and Lactation Considerations
The safety of semaglutide during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been established. If you’re pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding:
- Inform your healthcare provider immediately
- Discuss the potential risks and benefits of continuing or discontinuing treatment
- Consider alternative weight management strategies during this time
Remember: Weight loss during pregnancy is generally not recommended unless under specific medical guidance.
Conclusion
The semaglutide dosage chart for weight loss provides a structured approach to initiating and maintaining this innovative treatment. By following the recommended dosing schedule and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can maximize the benefits of semaglutide while minimizing potential risks and side effects.
Finding the Optimal Time
While the dosage chart provides a general framework, finding the optimal time to take semaglutide may require some personal experimentation. Consider factors such as:
- Your daily routine
- When you typically experience the most hunger
- How the medication affects your sleep patterns
Pro tip: Keep a journal during the first few weeks of treatment to track how you feel at different times of day. This information can help you and your healthcare provider determine the best timing for your doses.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Remember that the information provided in this article is general in nature and should not replace personalized medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen or if you have concerns about your treatment.
Regular check-ins with your healthcare team are crucial for:
- Monitoring your progress
- Addressing any side effects or concerns
- Making necessary adjustments to your treatment plan
- Ensuring you’re on track to meet your weight loss goals
Taking Control of Your Anxiety
While semaglutide can be a powerful tool for weight loss, it’s most effective when combined with lifestyle changes. To maximize your results:
- Follow a balanced diet: Focus on nutrient-dense, whole foods that keep you feeling satisfied.
- Stay active: Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Manage stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support your weight loss efforts.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support your body’s functions and help control hunger.
Remember, weight loss is a journey, and semaglutide is just one tool to help you along the way. Be patient with yourself, celebrate small victories, and don’t hesitate to reach out for support when you need it.
Takeaways
- The semaglutide dosage chart for weight loss involves a gradual dose escalation over 16 weeks, followed by a maintenance dose.
- Regular monitoring and follow-up with your healthcare provider are crucial for safety and effectiveness.
- Be aware of potential side effects and contraindications, and report any concerns to your healthcare provider promptly.
- Proper administration technique and storage are important for maximizing the benefits of semaglutide.
- Combine semaglutide treatment with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management for optimal results.
- Always follow your healthcare provider’s guidance and the patient information leaflet for safe and effective use of semaglutide.
By following these guidelines and working closely with your healthcare team, you can harness the power of semaglutide to support your weight loss journey and improve your overall health and well-being.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2021). FDA Approves New Drug Treatment for Chronic Weight Management, First Since 2014. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management-first-2014
Your trusted source for health info, offering expert advice, news, and tips to stay healthy and informed.