What Is Commonly Misdiagnosed as Pink Eye?
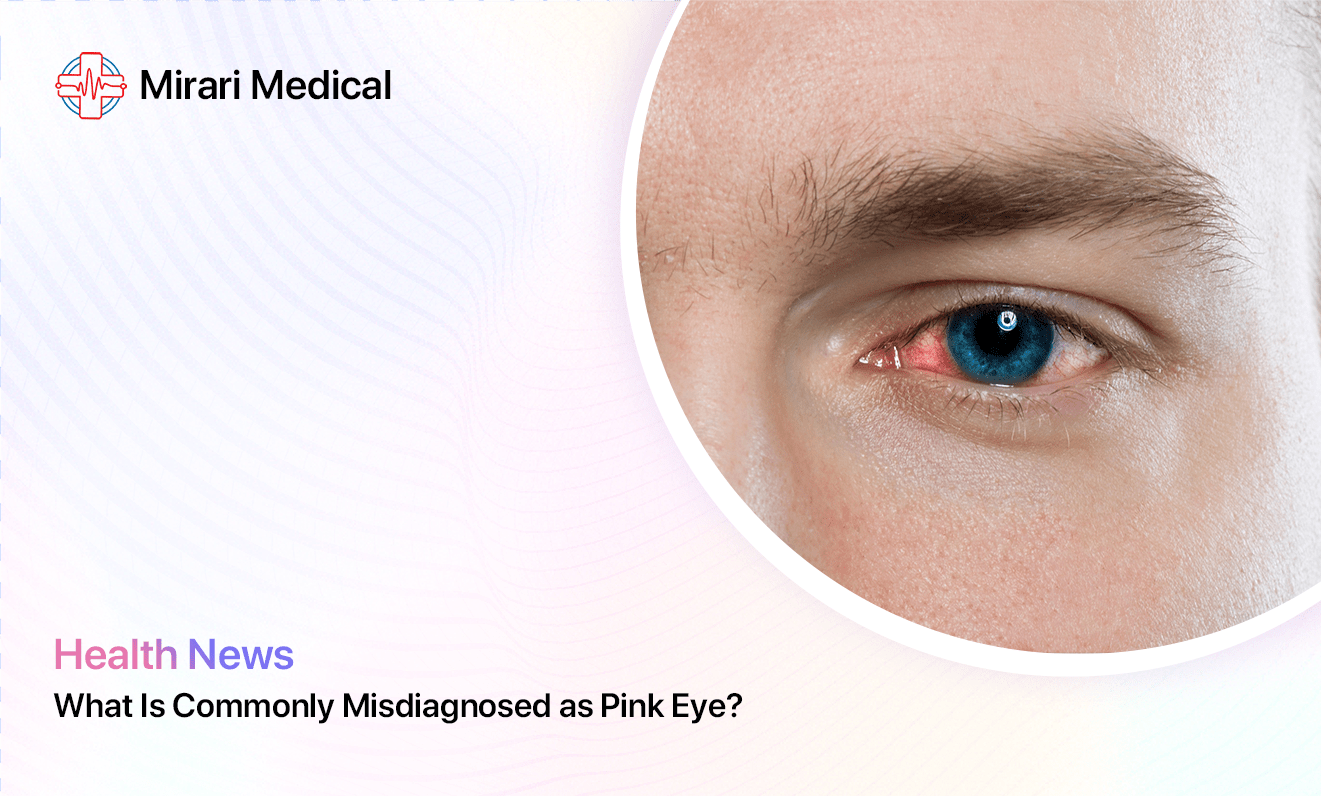
Pink eye, medically known as conjunctivitis, is a common eye condition that affects millions of people each year. Its hallmark symptoms of redness, itchiness, and discharge often lead to self-diagnosis or even misdiagnosis by healthcare providers. However, several other eye conditions share similar symptoms, making it crucial to receive an accurate diagnosis from an eye care professional. Misdiagnosed eye conditions can delay proper treatment and potentially lead to more serious complications.
Introduction
Definition of Pink Eye
Conjunctivitis, or pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin, clear tissue covering the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. This inflammation causes the blood vessels in the eye to become more visible, leading to the characteristic pinkness or redness associated with the condition. Pink eye can be caused by viruses, bacteria, allergens, or irritants, and it is highly contagious when caused by an infection.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Receiving an accurate diagnosis for pink eye is essential for several reasons:
- Proper treatment: Different causes of conjunctivitis require different treatments. For example, bacterial conjunctivitis may require antibiotic eye drops, while viral conjunctivitis typically resolves on its own.
- Preventing complications: Some eye conditions that mimic pink eye, such as keratitis or uveitis, can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
- Limiting the spread of infection: Infectious forms of conjunctivitis are highly contagious, so identifying and treating the condition promptly can help prevent its spread to others.
Common Conditions Misdiagnosed as Pink Eye
Several eye conditions share symptoms with pink eye, leading to potential misdiagnosis. Some of the most common conditions mistaken for conjunctivitis include:
Allergies
Allergic conjunctivitis occurs when the eyes react to allergens such as pollen, pet dander, or dust mites. This type of conjunctivitis is not contagious and often occurs seasonally or when exposed to specific triggers.
Symptoms of Allergic Conjunctivitis
- Itchy eyes
- Watery discharge
- Redness
- Swollen eyelids
Differences from Infectious Pink Eye
Allergic conjunctivitis typically affects both eyes and is accompanied by other allergy symptoms, such as sneezing or a runny nose. In contrast, infectious conjunctivitis often starts in one eye and may spread to the other, and it is not usually associated with other allergy symptoms.
Dry Eye Syndrome
Dry eye syndrome occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or when the tears evaporate too quickly. This can lead to eye irritation, redness, and a gritty or burning sensation.
Symptoms of Dry Eye
- Stinging or burning sensation
- Gritty feeling in the eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision
Causes and Risk Factors
Dry eye syndrome can be caused by various factors, including:
- Aging
- Certain medications (e.g., antihistamines, decongestants)
- Medical conditions (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome)
- Environmental factors (e.g., dry or windy conditions, prolonged screen time)
Keratitis
Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. This condition can be caused by infections, injuries, or wearing contact lenses for extended periods.
Symptoms of Keratitis
- Eye pain
- Redness
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Excessive tearing or discharge
Potential Complications
If left untreated, keratitis can lead to serious complications, such as corneal ulcers or scarring, which can permanently affect vision.
Iritis (Anterior Uveitis)
Iritis, also known as anterior uveitis, is an inflammation of the iris, the colored part of the eye. This condition can cause symptoms similar to pink eye, making it difficult to distinguish between the two.
Symptoms of Iritis
- Eye pain
- Redness
- Light sensitivity
- Blurred vision
- Small pupil
Importance of Prompt Treatment
Iritis requires prompt treatment to prevent complications such as cataracts, glaucoma, or permanent vision loss. Treatment typically involves corticosteroid eye drops to reduce inflammation.
Styes (Hordeolum)
A stye, or hordeolum, is a painful, red bump that develops near the edge of the eyelid. Styes are caused by a bacterial infection of the oil glands in the eyelid.
Symptoms of a Stye
- Red, painful bump on the eyelid
- Swelling of the eyelid
- Tenderness
- Sensitivity to light
Differences from Pink Eye
While a stye may cause redness and discomfort in the affected eye, it is usually localized to the eyelid and does not typically involve discharge or itching, which are common symptoms of pink eye.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the eyelids, often caused by a buildup of bacteria or dandruff on the eyelashes and eyelid margins. This condition can cause symptoms similar to pink eye, making it difficult to differentiate between the two.
Symptoms of Blepharitis
- Red, swollen eyelids
- Itching or burning sensation
- Flaky skin around the eyelashes
- Crusting on the eyelashes
- Sensitivity to light
Treatment Options
Treatment for blepharitis typically involves maintaining good eyelid hygiene, such as:
- Applying warm compresses to the eyelids
- Gently cleaning the eyelids with a mild soap or baby shampoo
- Using antibiotic ointments or oral antibiotics in severe cases
Pinguecula and Pterygium
A pinguecula is a yellowish, raised growth on the conjunctiva, usually near the cornea. A pterygium is a growth of the conjunctiva that extends onto the cornea. Both conditions can cause redness and irritation, mimicking the symptoms of pink eye.
Symptoms of Pinguecula
- Yellowish bump on the conjunctiva
- Redness
- Irritation
- Dryness
Differences from Pink Eye
Pinguecula and pterygium are typically localized growths that do not cause discharge or spread to the other eye, unlike infectious conjunctivitis.
Uveitis
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye that includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. This condition can cause symptoms similar to pink eye, but it is often more severe and can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Types of Uveitis
- Anterior uveitis (iritis)
- Intermediate uveitis
- Posterior uveitis
- Panuveitis (involving all layers of the uvea)
Symptoms and Risks
Symptoms of uveitis may include:
- Eye pain
- Redness
- Light sensitivity
- Blurred vision
- Floaters
Uveitis can be associated with systemic conditions such as autoimmune disorders or infections. If left untreated, it can lead to complications such as cataracts, glaucoma, or retinal detachment.
Contact Lens-Related Issues
Wearing contact lenses can sometimes cause eye irritation or infections that may be mistaken for pink eye.
Common Problems from Contact Lens Use
- Contact lens-induced acute red eye (CLARE)
- Giant papillary conjunctivitis (GPC)
- Corneal abrasions
- Corneal ulcers
Preventive Measures
To reduce the risk of contact lens-related issues:
- Follow proper lens care and hygiene practices
- Replace lenses as recommended by your eye care professional
- Avoid sleeping in contact lenses unless approved by your doctor
- Remove lenses if you experience any discomfort or redness
Diagnostic Approaches
Importance of Eye Examinations
To ensure an accurate diagnosis, it is essential to have a comprehensive eye examination by an eye care professional. During the exam, the doctor will:
- Review your medical history and symptoms
- Examine the external and internal structures of the eye
- Assess vision and eye pressure
- Use specialized instruments to visualize the eye’s surface and internal structures
Role of Ophthalmologists
Ophthalmologists are medical doctors who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases. They have the expertise to differentiate between various eye conditions and provide appropriate treatment.
Differentiating Factors for Diagnosis
Eye care professionals use several factors to differentiate between pink eye and other conditions:
- Onset and duration of symptoms
- Presence of discharge and its characteristics
- Involvement of one or both eyes
- Associated symptoms (e.g., pain, light sensitivity, vision changes)
- Response to treatment
Conclusion
Summary of Common Misdiagnoses
Pink eye is often confused with other eye conditions due to overlapping symptoms. Some of the most common conditions misdiagnosed as pink eye include:
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Dry eye syndrome
- Keratitis
- Iritis (anterior uveitis)
- Styes
- Blepharitis
- Pinguecula and pterygium
- Uveitis
- Contact lens-related issues
Call to Action for Seeking Professional Help
If you experience any symptoms of pink eye or other eye discomfort, it is essential to seek the advice of an eye care professional. Self-diagnosis or relying on online resources can lead to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment, potentially resulting in more serious complications.
Remember, your eye health is crucial to your overall well-being. By receiving prompt and accurate diagnosis and treatment, you can protect your vision and maintain healthy eyes for years to come.
Takeaways
- Pink eye is commonly misdiagnosed due to its similarities with other eye conditions.
- Accurate diagnosis is crucial for proper treatment and preventing complications.
- Common conditions mistaken for pink eye include allergies, dry eye syndrome, keratitis, iritis, styes, blepharitis, pinguecula, pterygium, uveitis, and contact lens-related issues.
- A comprehensive eye examination by an eye care professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- If you experience any symptoms of pink eye or other eye discomfort, seek professional help promptly to protect your eye health and vision.
Your trusted source for health info, offering expert advice, news, and tips to stay healthy and informed.
